Hook: In Houston, Texas, enough plastic waste is generated every day to fill a city block, yet mountains of bottles and bags continue to spill from bins, untouched by so-called “advanced” solutions. Can advanced recycling truly tackle this wave of waste, or is the magic nothing but smoke and mirrors? This article uncovers what’s really happening with Houston Texas advanced recycling plastic waste, offering a revealing look behind the city’s recycling promises versus reality.
Houston Texas Advanced Recycling: When Plastic Waste Piles Up Instead of Disappearing
"Every day in Houston, enough plastic waste is generated to fill a city block – much of it remains unrecycled." – Local Environmental Report
Opening Hook: Houston’s Startling Plastic Waste Crisis
Unprecedented surge in plastic waste
Advanced recycling promises vs. on-the-ground realities
Mounting public concern and skepticism
As plastic waste surges across Houston, the city’s ambitious advanced recycling program faces mounting scrutiny. Each week, the news is filled with images of bins and curbs overflowing—evidence that despite significant investment in chemical recycling and other cutting-edge technologies, much of Houston's plastic is still winding up in landfills or, worse, polluting local waterways and neighborhoods. According to reports by CBS News and Inside Climate News, solid waste management sites cannot keep up with the millions of pounds of plastic produced and discarded every month. Residents are left to wonder: Is the city’s recycling program actually solving the problem, or just dressing it up?
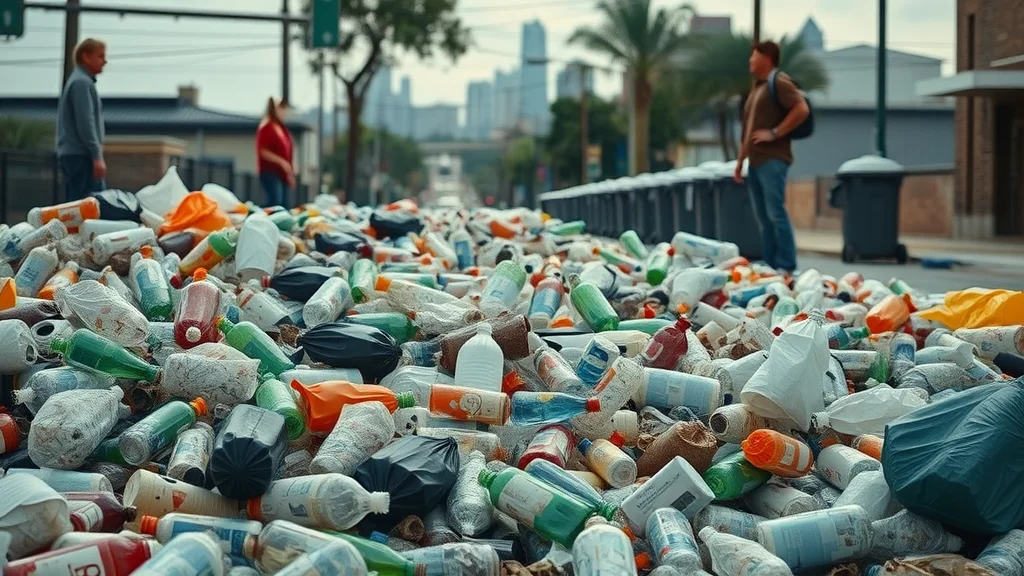

What You'll Learn About Houston Texas Advanced Recycling and Plastic Waste
The realities behind Houston Texas advanced recycling programs
How chemical recycling technologies work
Why plastic waste piles up despite ‘advanced’ solutions
Expert opinions and critical perspectives
This article dives deep into why Houston Texas advanced recycling plastic waste is piling up and keeps getting higher, even as the city rolls out new recycling collaborations like the Houston Recycling Collaboration with Cyclyx International. You will discover the truth behind flashy terms like “chemical recycling,” investigate the everyday realities at a recycling facility, and hear from both experts and everyday Houstonians. From technical limitations to environmental health risks, we explore why solutions touted as “magic” often fail to live up to expectations, and what else is needed to address the city’s plastic pollution.
For a closer look at the real-world challenges facing chemical recycling infrastructure, including recent project delays and their ripple effects on local waste management, you may find it useful to review this in-depth analysis of chemical recycling plant delays and their impacts. Understanding these setbacks can shed light on why Houston’s advanced recycling efforts have yet to deliver on their full promise.
Understanding Houston’s Advanced Recycling Program and Its Approach to Plastic Waste
How the Houston Texas Advanced Recycling Program Was Introduced
The City of Houston launched its advanced recycling initiative with fanfare, promising a revolutionary approach to plastic waste management. Partnerships formed with major names in oil and gas and chemical industries, including facilities backed by Cyclyx International and local players like Wright Waste Management. These recycling facilities were designed not just to sort, but to transform plastics via chemical recycling, breaking them down into raw materials for reuse. Official statements bragged of a new “circular economy” for Houston’s plastic waste. CBS News covered the story widely, highlighting city officials’ hopes that advanced processes would end the city’s reputation for failed fire and overburdened landfills. Despite this optimism, many residents began to notice that their recycling bins were still regularly overflowing.
Plastic Waste Management: Promises Made by Advanced Chemical Recycling
"Advanced recycling was hailed as a game-changer; yet, Houstonians witness little change in their overflowing waste bins." – Waste Industry Insider
Advanced recycling, particularly chemical recycling, promised to tackle what traditional recycling could not: difficult-to-recycle plastics like flimsy bags, shrink-wrap, and contaminated containers. The city invested in high-tech sorting facilities equipped with robotic arms and advanced sensors, aiming to divert millions of pounds of plastic from landfill each year. Proponents claimed these new processes would help alleviate plastic pollution while reducing reliance on virgin plastic production—creating benefits for both the environment and solid waste infrastructure. However, as inside climate news and environmental health groups quickly pointed out, the numbers told a different story: plastic continues to pile up, and contamination or technical flaws often mean far less is truly recycled than promised. This gap between expectation and result is at the heart of the public’s growing skepticism.

Plastic Waste: What the Data Says About Houston’s Advanced Recycling
Comparison Table: Plastic Waste Recycled in Houston Pre- vs. Post-Advanced Recycling Initiative |
|||
Time Period |
Total Plastic Waste Generated (Million Pounds) |
Plastic Waste Recycled (Million Pounds) |
Actual Recycling Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
Before Advanced Recycling (2018) |
60 |
9 |
15% |
After Advanced Recycling (2022) |
73 |
13 |
18% |
Advanced Recycling vs. Traditional Methods: Are We Really Managing Plastic Waste Better?
The data shows that, after substantial investment and publicity, Houston’s transition to advanced recycling increased the city’s total plastic recycling rate by just 3%. While this is technically an improvement, it is paltry compared to the millions of pounds still winding up in landfills or entering the environment unchecked. Traditional recycling programs struggled with low participation and contamination, but advanced recycling brought its own set of technical bottlenecks. Even with new facilities online, Houston Texas advanced recycling plastic waste piles up remains a stubborn headline. Many environmental groups argue that these small gains don’t justify the high costs, energy use, and ongoing emissions associated with high-tech solutions—a theme echoed in both climate news and local media.
Chemical Recycling in Houston: Promises Versus Performance
While chemical recycling sounded revolutionary, turning complex plastics back into base materials, its effectiveness in Houston remains limited. Technologies promise to repurpose pounds of plastic waste into new products or fuels, but technical glitches, contamination, and high energy requirements often reduce actual yields. Reports from Inside Climate News and Wright Waste Management show that only a small percentage of plastic entering these facilities emerges as truly reusable feedstock. More frequently, much is diverted back to landfill or incineration, undermining environmental health goals. Residents and stakeholders are increasingly asking if chemical recycling is the magic bullet they were promised, or just another stopgap with hidden environmental costs.
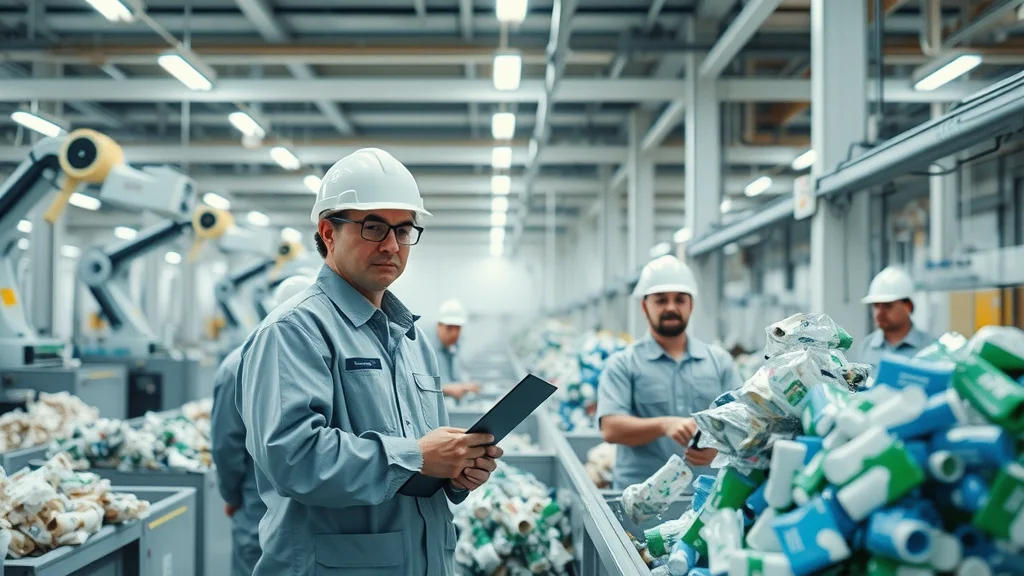
A Visual Tour of Chemical Recycling Operations
Step inside a Houston chemical recycling facility and you’ll find mountains of plastic streaming in from across Harris County. Conveyor belts, robotic sorters, and chemical treatment tanks attempt to process all shapes and types. While some plastics are successfully broken down and separated into reuse materials, a significant portion remains behind—unable to be processed, too contaminated, or simply not viable for conversion. Engineers and workers report frequent challenges with sorting, machine breakdowns, and unexpected residues, which the city’s waste management teams struggle to handle. Even with the most advanced systems, only a portion of what enters the facility leaves as a clean, marketable product; the rest adds to Houston’s mounting solid waste burden.
Why Houston Texas Advanced Recycling Struggles With Plastic Waste Piles
Operational Challenges: Sorting, Contamination, and Chemical Recycling Limitations
Inefficiencies in material sorting
Technical limits of chemical recycling
Unexpected environmental consequences
Advanced recycling requires meticulous sorting of plastic types, a process still prone to both human and machine error. Sorting facilities often miss items or inadvertently mix contaminated materials, reducing the effectiveness of chemical recycling. Even with robust technology, many plastics—especially multi-layer packaging—remain unrecyclable, ending up in landfills or, after a failed fire, incinerators. Numerous news stories have spotlighted these weaknesses, as has the experience of the city’s own wright waste management partners. Beyond technical snags, advanced recycling also brings unexpected environmental health risks: chemical byproducts, greenhouse gas emissions, and increased water usage—all issues that city planners and environmental groups struggle to address. The result? Despite lofty pledges, Houston's advanced recycling plastic waste piles up exactly as before, but now with a more complicated backstory.
Community Responses to Plastic Waste and Advanced Recycling
Public trust in Houston’s advanced recycling initiative has wavered as the effectiveness gap grows clearer. Many Houstonians, especially in diverse neighborhoods most affected by plastic pollution, gather at town halls to voice frustration and demand transparency from city officials and waste management partners. Local residents question whether money spent on new facilities or chemical recycling collaborations is delivering real-world results. Environmental health and environmental groups note that promises of near-instant technological fixes ring hollow when plastic continues to overflow bins and pollute creeks. At these meetings, calls for systemic change—like source reduction and improved composting—are rising, as citizens realize that high-tech recycling can’t alone turn back the plastic tide in Houston.
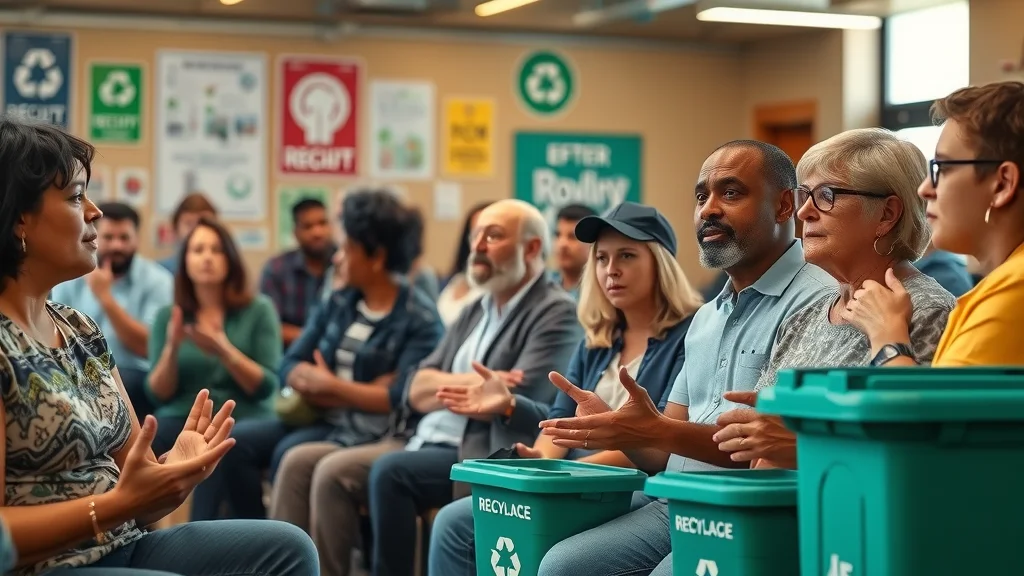

Plastic Waste, Advanced Recycling and its Environmental Impact in Houston
Houston’s Air & Water: Pollutants Linked to Chemical Recycling
"Despite advanced recycling technologies, plastic waste piles up while emissions quietly rise." – Independent Houston Environmentalist
The environmental health impacts of chemical recycling are under growing scrutiny in Houston, especially as more chemical recycling facilities come online near residential and sensitive ecological areas. Pollutants released during chemical breakdowns—such as volatile organic compounds and trace carcinogens—can drift into surrounding air and water tables, raising concerns for neighboring communities. Inside climate news and and CBS news have reported on rising emissions linked to these facilities, despite city assurances of strict controls. Environmental health advocates in Harris County are now pushing for comprehensive studies and independent monitoring to assess whether Houston’s recycling revolution is quietly creating a new, invisible form of plastic pollution in local air and waterways.
Unintended Consequences of Houston Texas Advanced Recycling
Beyond direct emissions, chemical recycling can shift environmental harm in ways that are harder to measure. Waste byproducts from chemical treatments often require further disposal in local landfills or can introduce harmful chemicals into water systems if mishandled. Additionally, the high energy consumption of continuous chemical processes means Houston’s climate news footprint expands just as the city tries to lower it. Environmental groups warn that the focus on “advanced” solutions distracts from the need for more fundamental change, such as reducing overall plastic production and improving waste management infrastructure. Without systemic reform, it’s possible advanced recycling could prolong, rather than solve, the city’s plastic waste crisis.

People Also Ask: Houston Texas Advanced Recycling and Plastic Waste
Is Houston’s advanced recycling program actually reducing plastic waste piles?
Analysis and evidence on actual waste reduction metrics.
Based on available data and public reports, Houston's advanced recycling plastic waste piles up has only shown marginal improvement. The city’s recycling rate crept up by 3% after the initiative, but much of the pounds of plastic waste still ends up in landfills or the environment. Real-world evidence from inside climate news and local environmental health groups suggests the impact on visible plastic waste piles is far smaller than promised in initial campaigns.
What are the main challenges facing Houston Texas advanced recycling plastic waste piles up initiatives?
Key operational, social, and environmental hurdles explained.
Major obstacles include inefficient sorting at recycling facilities, contamination of recyclable materials, and technical limits to chemical recycling processes. Socially, there’s growing skepticism among Houston residents who expect more visible change for their communities. On the environmental side, both emissions and chemical byproducts from chemical recycling raise public health concerns, especially for neighborhoods closest to these facilities. Persistent issues detailed by CBS News and wright waste management reveal just how complex true progress can be.
How does chemical recycling work and is it really effective in Houston?
Chemical breakdown of plastic waste and current effectiveness in local context.
Chemical recycling involves breaking down plastics at the molecular level using heat or solvents to produce either raw plastics or chemical feedstocks. In Houston, these facilities were highly publicized as a solution for hard-to-recycle plastics. In practice, their effectiveness is limited by input contamination, technical faults, and high costs, resulting in only a small fraction of plastic being truly recycled while much still goes to solid waste or emissions, as detailed by CBS News and environmental health studies.
Are there safer or better alternatives to advanced recycling for Houston’s plastic waste?
Exploring other proven or emerging strategies for plastic waste management.
Yes. Options like upstream waste reduction, shifting consumer habits, decentralized composting, improved material recovery at sorting facilities, and product redesign to avoid difficult plastics are gaining traction among leading environmental groups and inside climate news experts. While advanced recycling can play a role, most evidence suggests that real progress requires a broad, systemic rethink of both consumption and waste management across Houston.

Chemical Recycling Technology: The Key to Ending Houston’s Plastic Waste Problem?
Promises vs. Reality: What Stakeholders and Residents Report
The media narrative around chemical recycling paints it as a silver bullet, but voices on the ground present a more mixed reality. Industry stakeholders highlight gains in recycling certain plastics but acknowledge persistent issues such as high operational costs, energy demands, and frequent facility shutdowns due to contamination. Local residents—especially those living near recycling plants—cite health concerns, continued visible plastic waste piles, and a lack of clear reporting from city officials. There’s widespread agreement that the technology, while innovative, is not yet living up to the needs or expectations of the City of Houston and its stretched waste management systems.
The Most Persistent Myths About Houston Texas Advanced Recycling and Plastic Waste
Several myths obscure the public debate around Houston's advanced recycling plastic waste piles up. These include: “Everything put into the blue bin is recycled,” “Advanced recycling is carbon neutral,” and “Chemical recycling is safer than traditional methods.” Data from independent environmental groups and inside climate news reveals most plastic is still not recycled, while chemical processes often have significant greenhouse gas emissions and can generate hazardous byproducts. Dispelling these myths is crucial for making better decisions about Houston’s real waste management future.
Key Takeaways: Lessons From Houston’s Struggle With Advanced Recycling and Plastic Waste
Houston’s advanced recycling outcomes lag behind public expectations
Chemical recycling delivers mixed results for plastic waste
Systemic changes—not magic tech—may be needed
Frequently Asked Questions: Houston Texas Advanced Recycling and Plastic Waste Piles
Why does plastic waste continue to pile up in Houston?
Despite advanced recycling facilities, technical inefficiencies, material contamination, and high levels of plastic production mean most waste goes unrecycled and ends up in landfills or the environment.How much plastic waste is recycled in advanced recycling facilities?
Only a fraction of the total plastic waste—about 18% as of the most recent data—actually gets recycled in these facilities, with most still diverted to other disposal methods.Is chemical recycling safe for Houston communities?
While regulated, chemical recycling can release harmful pollutants and requires strict controls to protect environmental and community health, especially in surrounding neighborhoods.What can residents do to support better plastic waste management?
Residents can reduce their plastic use, support zero-waste initiatives, advocate for stronger local policies, and demand transparency from city officials and recycling operators.
Conclusion: The Ongoing Challenge of Houston Texas Advanced Recycling as Plastic Waste Piles Up
Houston’s experience shows that even the most advanced recycling technology cannot single-handedly solve the city’s plastic waste crisis. Comprehensive solutions and community-driven change remain critical.
If you’re interested in the bigger picture of how cities and communities can truly move the needle on plastic waste, it’s worth exploring the urgent need to expand our overall recycling capacity and rethink our approach to resource management. Discover actionable strategies and the latest innovations in unlocking the power of plastic recycling at scale. By understanding the broader landscape and embracing new solutions, Houston—and cities like it—can move beyond incremental gains and toward a more sustainable, circular future for plastic waste.
 Add Row
Add Row  Add
Add 




Write A Comment